Collagen has become a buzzword in the skincare and wellness world—but what exactly is it, and why is it so vital for healthy, youthful skin? This blog dives deep into the science of collagen, how it works, what depletes it, and how you can support your body’s natural production for radiant, resilient skin.
What is Collagen?
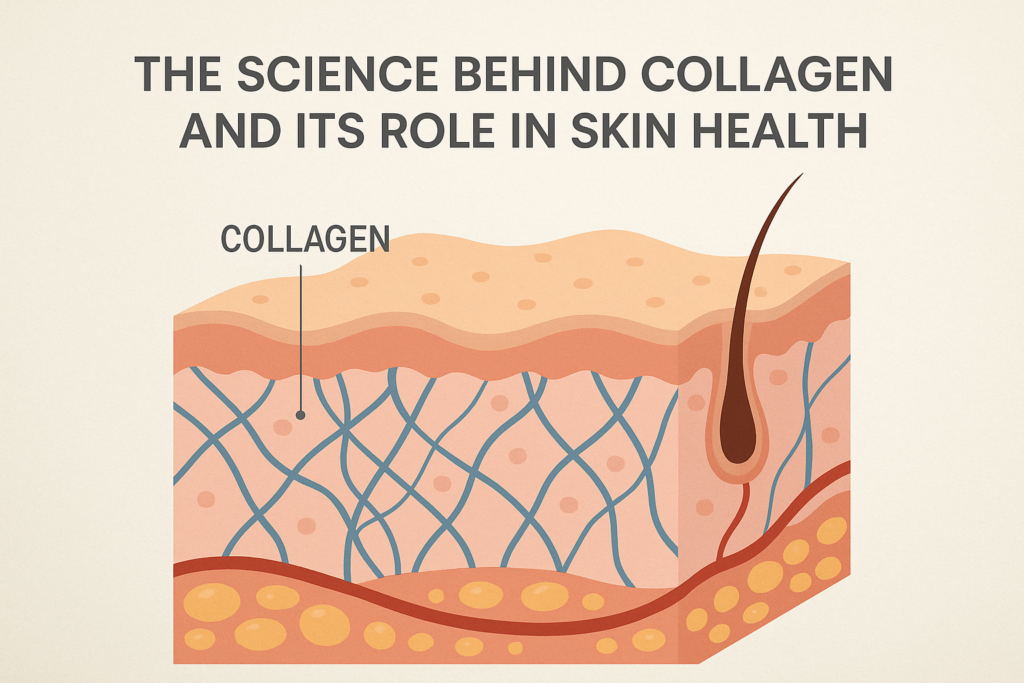
Collagen is the most abundant protein in the human body, accounting for about 30% of its total protein content. It serves as the primary structural component of connective tissues like skin, bones, tendons, and cartilage. In the skin, collagen works in harmony with elastin and hyaluronic acid to maintain firmness, hydration, and elasticity.
There are at least 28 types of collagen, but types I, II, and III are the most relevant for skin health. Type I collagen, in particular, is what gives skin its strength and structure.
How Collagen Supports Skin Health
Collagen plays multiple roles in skin health:
- Structural Support: It forms a fibrous network in the dermis, the middle layer of the skin, providing a framework for new cells and tissues.
- Elasticity & Firmness: Collagen fibers help the skin resist stretching and sagging, maintaining youthful plumpness.
- Wound Healing: Collagen is critical for skin regeneration, accelerating the healing of cuts, scars, and other injuries.
The Aging Process and Collagen Loss
Collagen production starts to decline around the age of 25. Factors like UV exposure, smoking, pollution, and stress accelerate this breakdown. As collagen depletes, signs of aging such as fine lines, wrinkles, and sagging become more apparent.
Here’s a look at how collagen levels change with age:
As shown in the chart, individuals in their 20s maintain 100% of their peak collagen levels. This drops to around 85% by the 30s and continues to decline rapidly with age.
External Factors That Damage Collagen
UV Radiation
The sun’s ultraviolet (UV) rays break down collagen fibers and trigger the production of abnormal elastin. This process is a leading cause of photoaging—premature aging of the skin due to sun exposure.
Smoking
Cigarette smoke contains over 4,000 chemicals, many of which are known to damage collagen and elastin. Smoking also reduces blood flow to the skin, depriving it of essential nutrients.
Pollution
Environmental pollutants produce free radicals, unstable molecules that damage collagen fibers and accelerate the skin aging process.
Poor Diet
A diet high in sugar and processed foods leads to the formation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs), which bind to collagen and make it stiff and brittle.
How to Boost Collagen Naturally
Nutrient-Rich Diet
Certain foods are particularly beneficial for collagen production:
- Vitamin C (oranges, strawberries, bell peppers): Essential for collagen synthesis.
- Zinc and Copper (nuts, seeds, whole grains): Aid in the formation and cross-linking of collagen fibers.
- Protein (chicken, fish, tofu): Provides amino acids like glycine, proline, and lysine—building blocks of collagen.
Collagen Supplements
Hydrolyzed collagen peptides are a popular supplement format. Research suggests they may help increase skin elasticity, hydration, and dermal collagen density over time.
A study published in the Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology found that oral collagen supplements significantly improved skin elasticity and hydration after just 12 weeks. Read the full study here.
Topical Products
Retinoids (vitamin A derivatives) stimulate collagen production at the cellular level. Peptides and antioxidants like vitamin C and niacinamide can also be effective.
Lifestyle Adjustments
- Use Sunscreen Daily: Broad-spectrum SPF protects against UV-induced collagen breakdown.
- Quit Smoking: Eliminates toxins that directly degrade collagen.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress elevates cortisol levels, which can hinder collagen formation.
Debunking Collagen Myths
Myth 1: Collagen creams can replace lost collagen.
Reality: Collagen molecules are too large to penetrate the skin. Topical collagen has limited efficacy unless paired with skin-penetrating peptides.
Myth 2: More collagen means better skin.
Reality: Collagen must be absorbed and utilized properly. Supportive nutrients and healthy habits are key to effectiveness.
Myth 3: Vegan diets can’t support collagen.
Reality: While collagen itself is animal-derived, vegans can promote natural production through plant-based sources of vitamin C, zinc, and amino acids.
Emerging Trends in Collagen Research
- Marine Collagen: Derived from fish skin and scales, it’s more bioavailable than bovine sources.
- Stem Cell Therapy: Shows promise in stimulating fibroblasts, the cells that produce collagen.
- Microneedling and Lasers: Trigger a controlled skin injury response that enhances collagen regeneration.
For deeper scientific insights, you can explore ongoing research by the National Institutes of Health.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: How long does it take to see results from collagen supplements?
A: Most studies show visible improvement in skin elasticity and hydration within 8–12 weeks of consistent use.
Q: Is collagen safe for everyone?
A: Generally, yes. However, people with food allergies or sensitivities should read labels carefully, especially with marine or bovine collagen.
Q: Can you regain lost collagen?
A: While you can’t fully restore lost collagen, you can significantly boost production through diet, supplements, and skin treatments.
Q: What’s the best time to take collagen supplements?
A: Many experts recommend taking them on an empty stomach, ideally in the morning, for optimal absorption.
Q: Does bone broth contain collagen?
A: Yes, bone broth is a natural source of collagen, gelatin, and amino acids beneficial for skin, joints, and gut health.
Conclusion
Collagen is the cornerstone of youthful, healthy skin. While aging and environmental stressors are inevitable, adopting collagen-friendly habits—from smart nutrition and quality skincare to protective measures—can go a long way in preserving your skin’s strength and vitality. With science-backed strategies and a proactive approach, glowing skin can be more than just a beauty goal—it can be your new normal.